ETH AI Digest: #16
Demonstration-based robot control, distortion-free video stabilization with 3D Gaussians, and internal probes catch LLM math errors
In this week's digest:
Teaching Robots Through Demonstration — DEMONSTRATE enables zero-shot language-to-robot control by learning from human demonstrations, eliminating the need for expert prompt engineering
3D-Grounded Video Stabilization — GaVS uses Gaussian Splatting to stabilize shaky videos without distortion or cropping, outperforming existing methods in challenging dynamic scenes
Detecting Math Errors in LLMs — Simple probes decode correct answers from language model internals with 90%+ accuracy, enabling error correction through selective re-prompting
Selected Papers of the Week
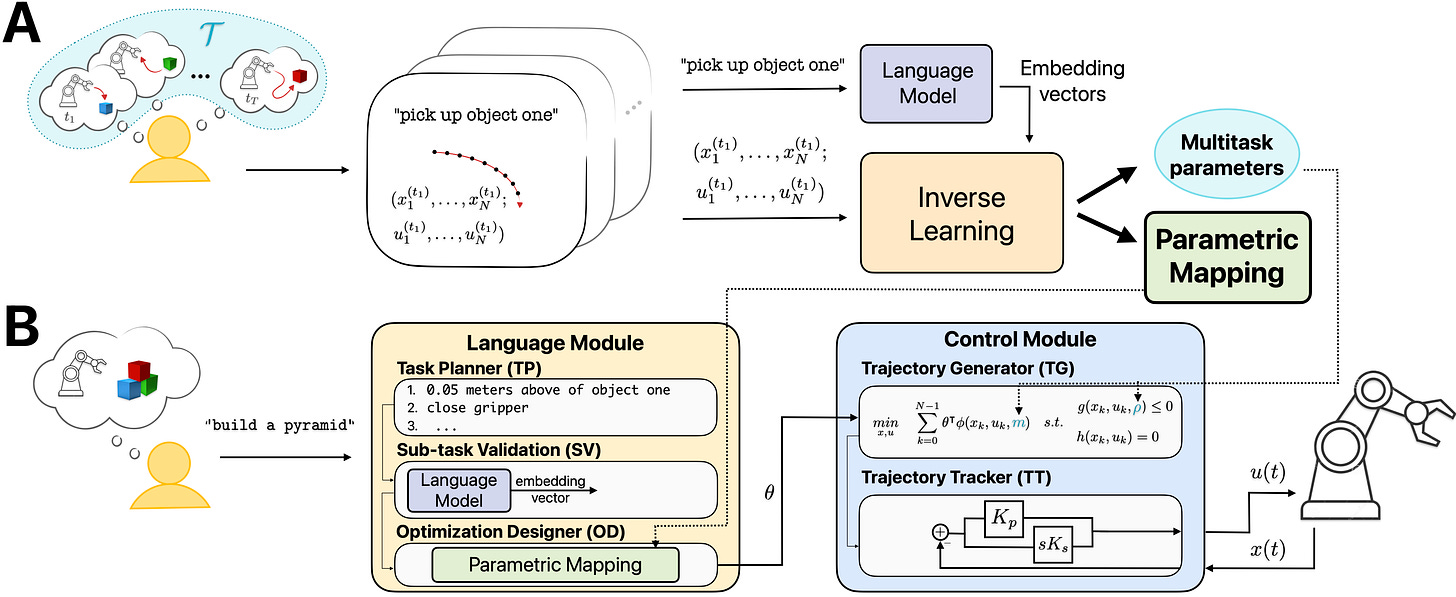
1. DEMONSTRATE: Zero-shot Language to Robotic Control via Multi-task Demonstration Learning
Teaching robots tasks through demonstrations instead of engineering complex prompts for language models.
✍️ Authors: Rahel Rickenbach, Bruce Lee, René Zurbrügg, Carmen Amo Alonso, Melanie N. Zeilinger
🏛️ Lab: Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control
⚡ Summary
DEMONSTRATE addresses the challenge of using natural language to control robots without requiring expert-designed prompts for language models.
The system learns from human demonstrations of subtasks, mapping language embeddings directly to control parameters using inverse reinforcement learning and multitask learning.
This approach enables robots to perform complex tasks while detecting potential hallucinations before execution.
Experiments show comparable or better performance than existing methods while reducing reliance on engineering expertise.
2. GaVS: 3D-Grounded Video Stabilization via Temporally-Consistent Local Reconstruction and Rendering
Stabilizing shaky videos with 3D Gaussian Splatting for distortion-free, full-frame results without additional sensors.

✍️ Authors: Zinuo You, Stamatios Georgoulis, Anpei Chen, Siyu Tang, Dengxin Dai
🏛️ Lab: Computer Vision and Learning Group
⚡ Summary
GaVS introduces a novel 3D-grounded approach to video stabilization that minimizes distortions and preserves full frames without additional sensors.
The method reconstructs local 3D scenes using Gaussian Splatting primitives and renders stabilized frames at smoothed camera poses.
Test-time optimization with multi-view dynamics-aware supervision ensures temporal consistency across reconstructions.
Extensive evaluations show GaVS outperforms state-of-the-art methods in balancing stability, distortion reduction, and geometry consistency, especially in challenging scenes with complex camera motions and dynamics.
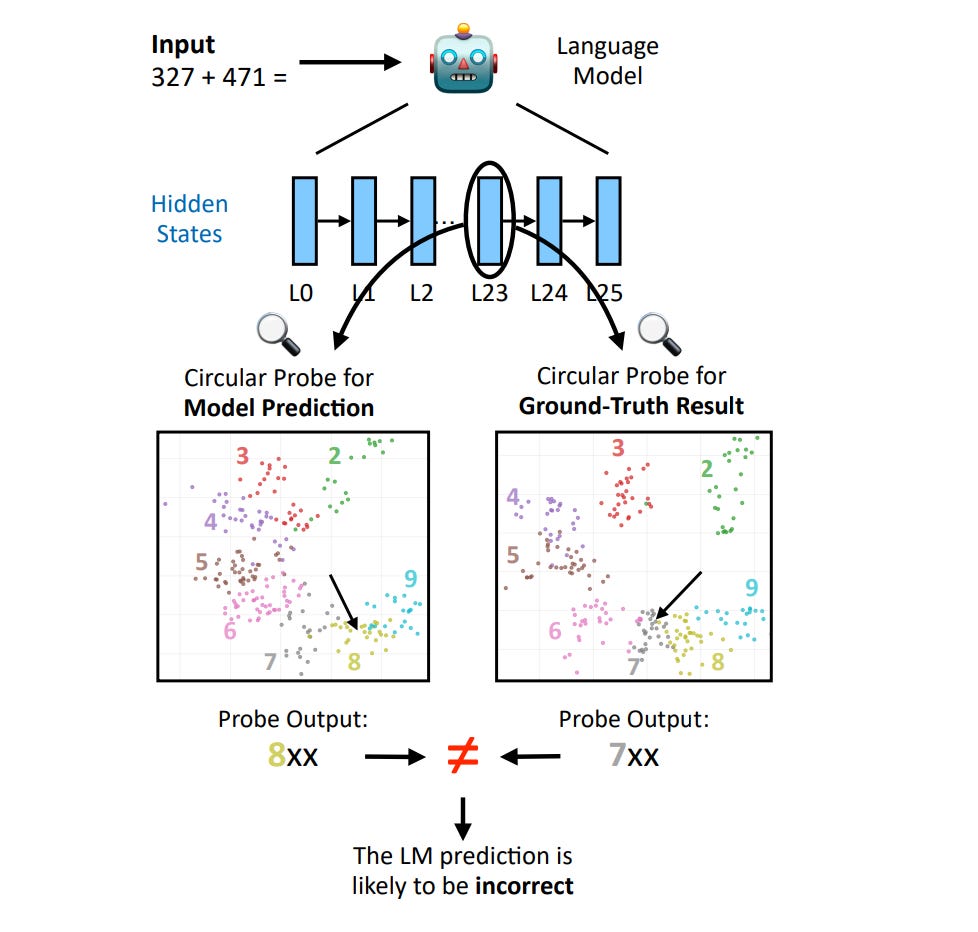
3. Probing for Arithmetic Errors in Language Models
Simple probes reveal hidden mathematical knowledge in language models, enabling error detection and correction.
✍️ Authors: Yucheng Sun, Alessandro Stolfo, Mrinmaya Sachan
🏛️ Lab: Language, Reasoning and Education Lab
⚡ Summary
This paper investigates whether language models' internal activations can detect arithmetic errors before they appear in outputs.
Researchers develop lightweight probes that accurately decode both model predictions and correct answers from hidden states with over 90% accuracy.
These probes generalize from simple arithmetic to complex chain-of-thought reasoning, revealing consistent internal representations across contexts.
When used to guide selective re-prompting, the probes can correct erroneous reasoning steps without compromising correct ones.



